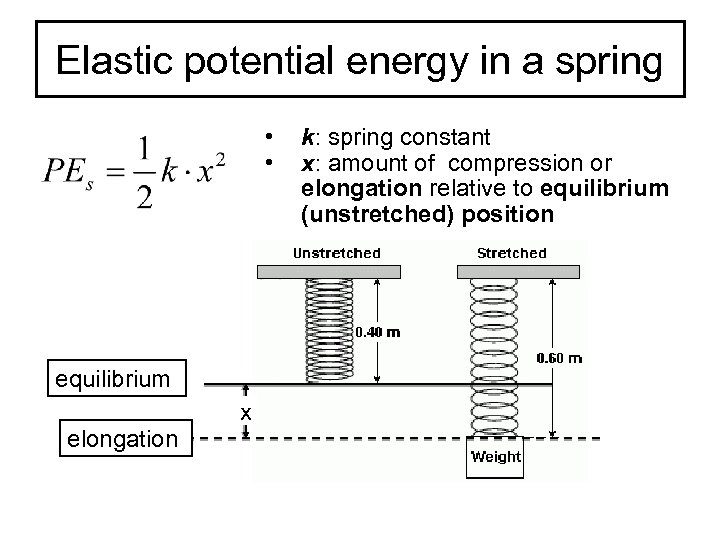
When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy . when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. If a spring is not stretched or. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\).
from ceqefcim.blob.core.windows.net
the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. If a spring is not stretched or. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary;
Does A Compressed Spring Have Energy at Alyce Wilson blog
When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; Hence the kinetic energy is zero. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. If a spring is not stretched or. when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lesson 15 Work and Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7055297 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. When it. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Springs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1426325 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). explain the. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From dotemwcieco.blob.core.windows.net
Does A Compressed Spring Have Energy at Anna Dudley blog When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. If a spring is not stretched or. Here,. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Work and Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4524294 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy Hence the kinetic energy is zero. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. If a spring is not stretched or. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; a spring’s. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT More Conservation of Mechanical Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6205783 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From lambdageeks.com
15 List of Potential Energy to Energy Example When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. If a spring is not stretched or. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. when a spring is compressed or. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 7 Potential energy and energy conservation PowerPoint Presentation ID4120420 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy If a spring is not stretched or. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; explain the potential. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Cole’s House of Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2854151 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. If a spring is not stretched or. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; Hence the kinetic energy. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From ck12.org
Spring Potential Energy Overview When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.meritnation.com
explain the potential energy of a spring Physics Work Energy And Power 8025 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy Hence upon release, this energy converts into. Hence the kinetic energy is zero. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. If a spring is not stretched or. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Types of Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6299241 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy Hence the kinetic energy is zero. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; the potential energy v(x) of the spring is. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.youtube.com
Potential Energy of a Spring Force YouTube When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy If a spring is not stretched or. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. the potential energy. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From slideplayer.com
Chapter 6 Work and Energy ppt download When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. If a spring is not stretched or. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.youtube.com
Potential energy stored in a spring Work and energy Physics Khan Academy YouTube When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; If a spring is not stretched or. the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDThe potential energy of a stretched spring is positive. Is the potential energy of a When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. Hence upon release, this energy converts into. a spring’s potential energy is stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.bartleby.com
Spring Potential Energy bartleby When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy the potential energy stored in a spring is \(\mathrm{pe}_{\mathrm{el}}=\frac{1}{2} k x^{2}\). Hence the kinetic energy is zero. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; Hence upon release, this energy converts into. the potential energy v(x) of. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 8 Conservation of Energy PowerPoint Presentation ID3523342 When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy the potential energy v(x) of the spring is considered to be zero when the spring is at the equilibrium position. when a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores potential energy. When it is extended to a displacement x, the ends are stationary; the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.
From www.youtube.com
Spring Energy YouTube When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy the spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. Here, we generalize the idea to elastic potential energy for a deformation of. explain the potential energy of a spring in terms of its compression when hooke’s law applies. If a spring is not stretched or. the potential. When A Spring Is Compressed What Happens To The Potential Energy.